- Medical Services
- Breast Care
- Specialties & Services
- Automated Breast Ultrasound
Automated Breast Ultrasound (ABUS)
ABUS provides supplemental screening for women with dense breasts. It is offered at the NMMC Breast Care Center in Tupelo.
Schedule your mammogram today
Innovative Technology Improving Breast Cancer Detection
The NMMC Breast Care Center offers automated breast ultrasound (ABUS) to supplement screening mammography for women with dense breasts, improving their overall breast cancer detection rate.
Mammogram + ABUS for Dense Breasts
Women diagnosed with dense breasts still need annual screening mammograms as recommended for all women over age 40 by the American College of Radiology. Supplemental screening with automated breast ultrasound works in tandem with mammography to improve breast cancer detection rates in women with dense breasts. Although the mammogram of a dense breast tissue may not show lumps as clearly as those with less dense breast tissue, mammography remains our best screening technique in all women. Additionally, there are some conditions that are only well seen with mammography including breast microcalcifications, which can be a very early sign of breast cancer. ABUS is not a substitute for screening mammograms.
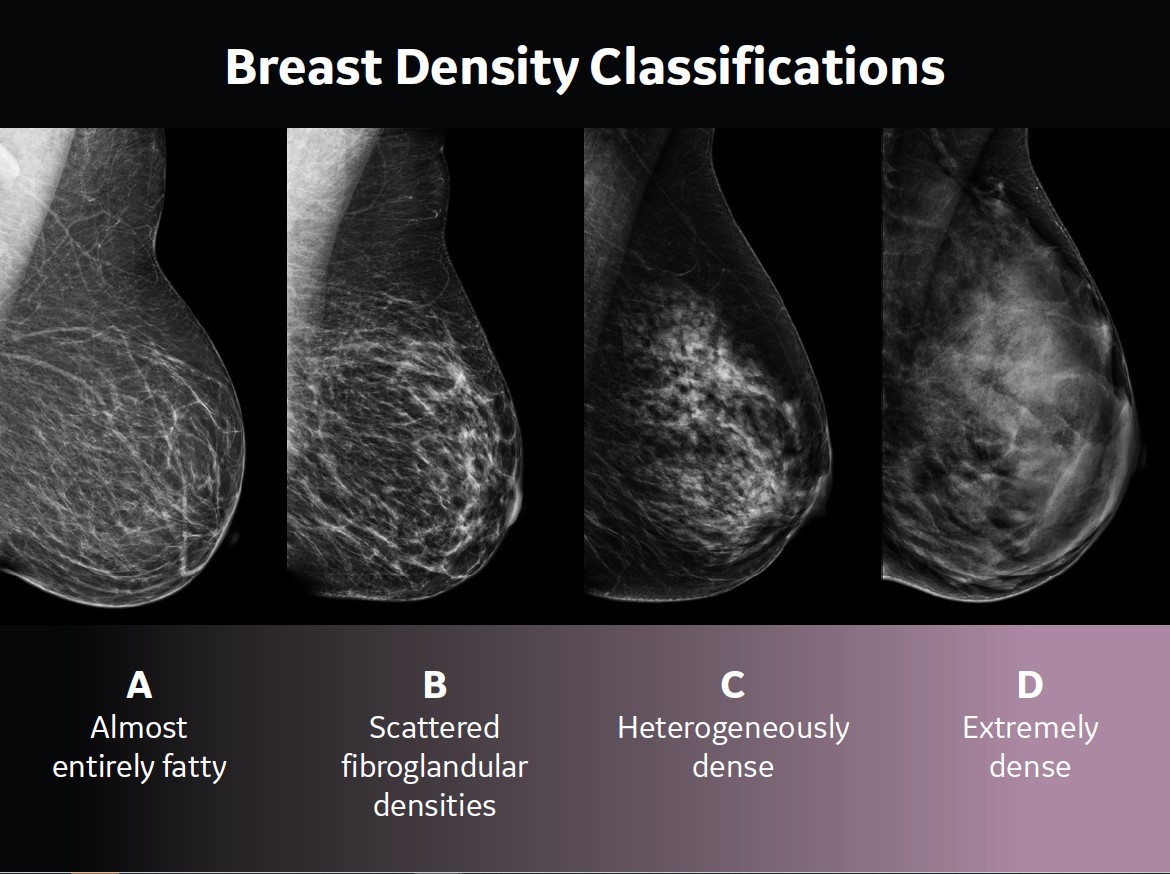
Breast tissue consists of two types: fatty and fibroglandular. If more than 50% of your breast is made of fibroglandular tissue, then your breasts are classified as dense. Key facts about breast density:
Dense breast tissue can’t be identified by touch or visual exam.
Density is diagnosed with mammography.
Dense breast tissue is not abnormal.
More than 40% of U.S. women have dense breasts.
Women often shift from dense to intermediate to low density during their lifetime, but changes occur at different times for each woman. Density can change with:
Pregnancy
Lactation
Menstrual cycle
Weight loss/gain
Hormone use
Surgery
Radiation treatment
Age
Dense breast tissue can make a mammogram harder to read. On an X-ray mammogram, fatty breast tissue appears gray, while both dense breast tissue and cancers show up as white. That means a cancer can easily hide in a background of dense breast tissue since they both appear white.
Dense breast tissue can’t be identified by touch.
Density is diagnosed with mammography.
Women with dense breast tissue have a 4-6 times higher risk of breast cancer.
What is ABUS?
Ultrasound is widely used by medical professionals as a non-invasive imaging technology. It uses sound waves to examine structures inside the body.
ABUS provides a complete ultrasound evaluation of the entire breast. Combined with your screening mammogram, it improves the overall sensitivity by 26.7% and increases the overall breast cancer detection rate for women with dense breasts.
For an ABUS exam, you will recline on your back.
A layer of ultrasound gel is applied to the breast.
A scanner is firmly positioned on the breast to acquire the images.
It takes about 15 minutes for a single breast or about 30 minutes for both.
ABUS is covered by most insurance if you meet screening criteria.
Subject to copays and deductibles
Check with your insurance provider to avoid unexpected fees
Out-of-pocket/Opt-Out cash price available for self-pay and high deductible plan patients
Related Locations
Upholding high standards for comprehensive breast care
Patient Stories

Mammograms Are Not Optional
Paige McFall was determined to beat her aggressive breast cancer.

‘I Thought What I Found Would Go Away, But it Didn’t'
Like many busy women, Debbie Cochran put off getting her annual mammogram.

‘I Was Fortunate to Catch it as Early as We Did’
If Anita Monroe had put off her mammogram, her prognosis would not be so positive.

‘If Something Is Not Right, Get Checked’
Shirlette Judon celebrating 16 years as breast cancer survivor

Mammograms Are Not Optional
Paige McFall was determined to beat her aggressive breast cancer.

‘I Thought What I Found Would Go Away, But it Didn’t'
Like many busy women, Debbie Cochran put off getting her annual mammogram.

‘I Was Fortunate to Catch it as Early as We Did’
If Anita Monroe had put off her mammogram, her prognosis would not be so positive.

‘If Something Is Not Right, Get Checked’
Shirlette Judon celebrating 16 years as breast cancer survivor
Related Resources
View AllBreast cancer screening matters. Annual screening with mammography is recommended starting at age 40 for those at average risk.











