How to Spot Skin Cancer at Any Age
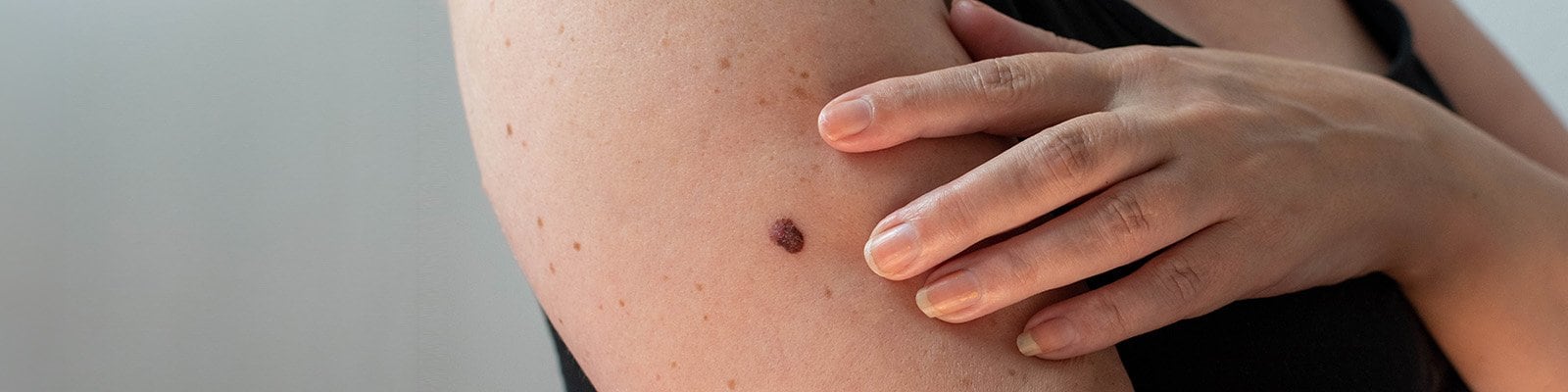
Monthly skin checks and knowing your ABCDEs can help catch skin cancer in its earliest, most treatable stage.
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer, and more than one in five Americans will develop skin cancer by age 70.
Knowing what to look for can be life-changing. Early detection means easier to treat. When detected early, the five-year survival rate for melanoma is 99%, according to the Skin Cancer Foundation.
Your primary care provider may include a skin exam as part of your annual wellness check. However, you will want to check yourself monthly.
Know your ABCDEs
You can use the ABCDE rule to check your moles for the following signs:
Asymmetry: If one part of the mole doesn’t match the other.
Border: The edges of your mole are irregular.
Color: The color of your mole or spot changes or is not the same all over.
Diameter: The spot or mole is larger than a pencil eraser.
Evolving: The mole is changing in size, shape or color.
Risk Factors
While anyone can develop skin cancer, certain factors increase your risk:
- A lighter natural skin color
- Skin that burns, freckles, reddens easily or becomes painful in the sun
- Blue or green eyes
- Blond or red hair
- Certain types and a large number of moles
- A history of sunburns or tanning
- Family and personal history of skin cancer
- Older age
Indoor tanning
The use of tanning beds and sun lamps dramatically increases your risk of skin cancer. The International Agency for Research on Cancer places indoor tanning on par with cigarettes and plutonium as cancer-causing agents. Indoor tanning particularly increases the risk of developing skin cancer before age 40, according to the Skin Cancer Foundation.
Reduce your risk
The three most common kinds of skin cancer – basal cell, squamous cell and melanoma – are associated with exposure to ultraviolet light from the sun. Managing your exposure and avoiding sunburns significantly reduces your risk.
- Reduce sun exposure, especially between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Wear clothing that protects your skin such as long sleeves, long pants and wide brim hats.
- Use a broad-spectrum SPF 15 sunscreen and reapply frequently when outdoors.
- Wear sunglasses with a UV filter to protect your eyes and the skin around your eyes
Remember, not all skin cancers look like the descriptions above so it’s important to contact your health care provider if you see anything that concerns you.